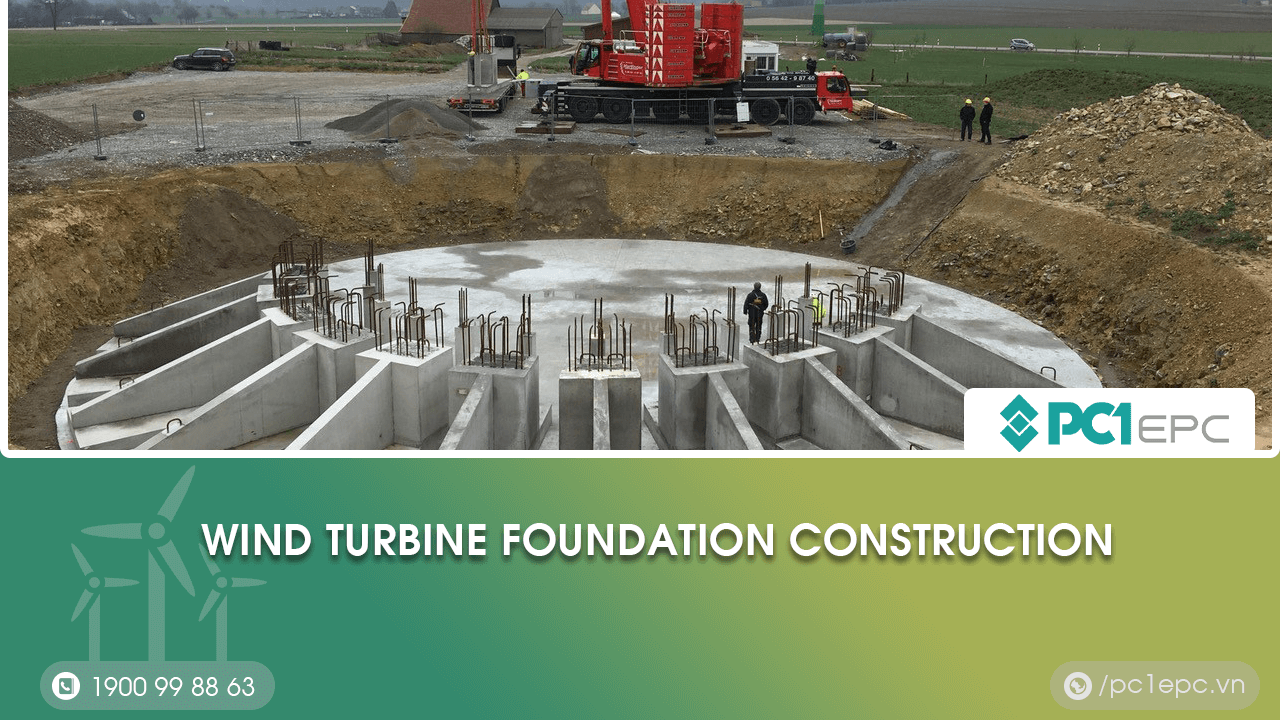
Wind turbine foundation construction refers to the process of building a solid and stable foundation for wind turbines, to ensure their safe and efficient operation. The foundation supports the weight of the wind turbine and its components, as well as the forces exerted by the wind.
The importance of wind turbine foundation construction cannot be overstated. A properly designed and constructed foundation ensures the long-term stability and safety of the wind turbine, minimizes maintenance costs, and maximizes energy production. A poorly designed or constructed foundation, on the other hand, can lead to structural failure, decreased energy output, and safety hazards for workers and the surrounding environment.
Wind turbine foundation construction process
Site selection and preparation
- Search and select a suitable location for the wind turbine and foundation construction.
- Perform site preparation tasks such as soil sampling, terrain assessment, and evaluation of the surrounding environment.
Soil investigation and analysis
- Conduct soil investigations to ensure that the foundation can withstand the load and impact of the wind turbine.
- Analyze the soil parameters to make appropriate design decisions.
Design of foundation and structural elements
- Design and calculate the foundation structure to ensure stability and load-bearing capacity of the wind turbine.
- Design the structural elements including tower, base, bracing, blades, and lightning protection system.
Materials and equipment needed for construction
- Choose appropriate materials for the wind turbine foundation and structure, including concrete, steel, and drilled piles.
- Arrange and prepare necessary equipment and machinery for the construction of the foundation and structure.
Excavation and installation of foundation elements
- Carry out excavation and installation of foundation elements.
- Install structural elements such as tower, base, bracing, blades, and lightning protection system.
Backfilling and compacting
- Perform backfilling and compaction around the foundation to ensure stability and load-bearing capacity of the wind turbine.
Types of wind turbine foundations
Shallow foundation
- Also known as a spread footing, this type of foundation is commonly used for small wind turbines.
- The foundation spreads the weight of the wind turbine over a large area to increase stability.
Deep foundation
- This type of foundation is used for larger wind turbines.
- It transfers the weight of the turbine to deeper layers of soil to increase stability and load-bearing capacity.
Pile foundation
- Pile foundations are commonly used for offshore wind turbines.
- They consist of vertical columns (piles) that are driven deep into the seabed to support the wind turbine.
Gravity foundation
- Also known as a ballasted foundation, this type of foundation is commonly used for large land-based wind turbines.
- It consists of a massive concrete block that is used to anchor the wind turbine in place.
Factors affecting wind turbine foundation construction
Wind turbine design and capacity
- These factors affect the foundation structure and the requirements for load and stability of the wind turbine.
Soil characteristics
- The soil characteristics at the foundation site affect the stability and load-bearing capacity of the wind turbine.
Site location and terrain
- The site location affects the transmission of the wind turbine loads to the foundation.
- The terrain of the site may require adjustments to the foundation design.
Environmental factors
- These factors include environmental requirements such as noise, flora and fauna, and environmental protection regulations.
Construction timeline and budget
- The construction timeline and budget affect the choice of technical solutions and construction materials and may affect the efficiency of the wind turbine foundation construction process.
Safety considerations during wind turbine foundation construction
Personal protective equipment (PPE)
- Workers should wear appropriate PPE, such as hard hats, safety glasses, gloves, and steel-toed boots.
- Additional PPE may be necessary, depending on the specific hazards present at the construction site.
Hazard identification and mitigation
- Potential hazards at the construction site should be identified and assessed, including risks related to falls, equipment, and electrical hazards.
- Measures should be put in place to mitigate these hazards, such as fall protection systems, lockout/tagout procedures, and proper equipment maintenance.
Emergency response planning
- An emergency response plan should be in place, outlining procedures for responding to accidents or incidents on site.
- Workers should be trained on the emergency response plan and should know how to respond in case of an emergency.
Related post: Wind farm construction – The rising strength of EPC PC1