A wind turbine with blades is extremely complex and expensive to build. Therefore, they become one of the most expensive wind power equipment. So, are you curious about what materials the engineers designed and manufactured the wind turbine blades made of? And what are their specific uses? What are the advantages and disadvantages of vertical-axis wind turbines? Let’s find out through the article below.
What material are the wind turbine blades made of?

At first glance, wind power propellers have a similar shape to airplane wings, so many people often mistakenly think they are made of the same material. In fact, the composite material to make the blades of wind turbine blades consists of glass and carbon fiber bonded together with adhesives.
Size and environment will affect the proportions of each material. Wind turbine blades in high wind speed areas will be made differently from wind turbine blades in low wind speed areas. The larger the turbine, the harder its blades are made.
In the early days, wind turbine blades were made of aluminum. But gradually, the engineers realized that aluminum was too heavy and needed time to accelerate. Instead, composite materials made of glass and carbon fiber can accelerate rapidly as wind speeds increase. It helps the wind turbine blades keep a constant speed and reduces the overall stress of the turbine.
In the past, after the end of the life cycle, unlike the column and motor housing that can be largely recycled, wind turbine blades are often sent to a landfill because the cost of removing the adhesive is too expensive. However, wind turbine blades make up 10% of fiber-reinforced materials in Europe, and the problem is exacerbated as more turbines reach the end of their lifecycles. Therefore, a way to change the adhesive has been sought to make it easier to recover the propeller parts, allowing them to be recycled and used for other purposes.
What is the function of wind turbine blades?
Although there are many types of wind turbines, they all operate on the same premise which is to use wind power. Basically, wind turbine blades get a kinetic energy from the wind, causing them to rotate. This kinetic energy is similar in nature to the lift force of an airplane wing since the wind turbine blades also have a similar profile. This rotation then generates electricity.
Technically, wind turbines usually consist of 2 to 3 blades. These blades rotate around a rotor connected to the main shaft of the generator. The kinetic energy generated when the wind turbine blades rotate will be rotated by the generator shaft. From there, generate electricity.
Vertical axis wind power propeller
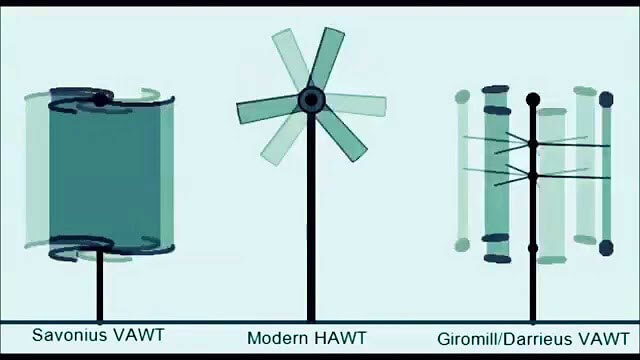
Today’s vertical axis wind turbines are mainly based on two operating principles: using drag or using the lift of the wind. Representing these two types of operating principles are the Savonius and Darrieus wind turbines.
The Savonius turbine has the simplest design and is composed of two or more semi-cylindrical buckets, using wind resistance to rotate the vertical axis connected to the generating equipment.
Whereas the Darrieus type consists of a vertical shaft and the blades are arc-shaped, with the ends of the blades attached to the top and bottom of the vertical shaft. The movement of these blades against the direction of the wind creates an aerodynamic force on the shaft, causing the blades to rotate.
Advantages of vertical axis wind turbine blades
Vertical-axis wind turbines have many advantages over traditional horizontal-axis wind turbines, especially when installed in residential areas. It is suitable for winds with unstable speeds, unlike horizontal axis wind turbines, which must be placed on a high tower to generate enough electricity.
Compared with horizontal axis wind turbines, vertical axis wind turbines can start operating at a lower wind speed and independent of the wind direction. This helps the vertical axis wind power propellers to be commonly installed in small areas, residential areas, and on the roofs of buildings with a capacity of only a few kW to several hundred kW.
Meanwhile, a large horizontal axis wind turbine with blades perpendicular to the wind direction will have a higher efficiency, and generate more electricity with a capacity of 3 – 4 MW, but its requirement is to be installed. on high altitude and requires a larger area of use, forming large wind power farms.
Limitations of vertical axis wind turbine blades
In addition to the above advantages, the vertical axis wind turbine also has limitations.
The first is poor rotational efficiency leading to low power generation efficiency and low available wind speed due to often underground installation.
Because they are often installed in residential areas, the components are prone to wear and tear due to the impact of the surrounding environment, and the conversion efficiency from wind energy to electrical energy is lower than that of horizontal axis wind power blades (average from 10 to 40% versus 50%).
Finally, the vertical axis wind power propeller must have a self-starting mechanism because low wind speeds can hardly make torque.
Final thoughts
Above is a summary of some necessary information to answer questions about the materials and effects of wind turbine blades as well as learn more about the advantages and disadvantages of vertical axis wind turbine blades. You can find more articles in the PC1 news section!
See more: Energy storage solutions provided by PC1 Group


