Have you ever heard about the term “wind farm capacity factor”? Or have you ever wondered about wind farms vs. solar farms—which is better? In this article, we will address these questions for you.
Wind farm capacity factor
What is a wind farm capacity factor?
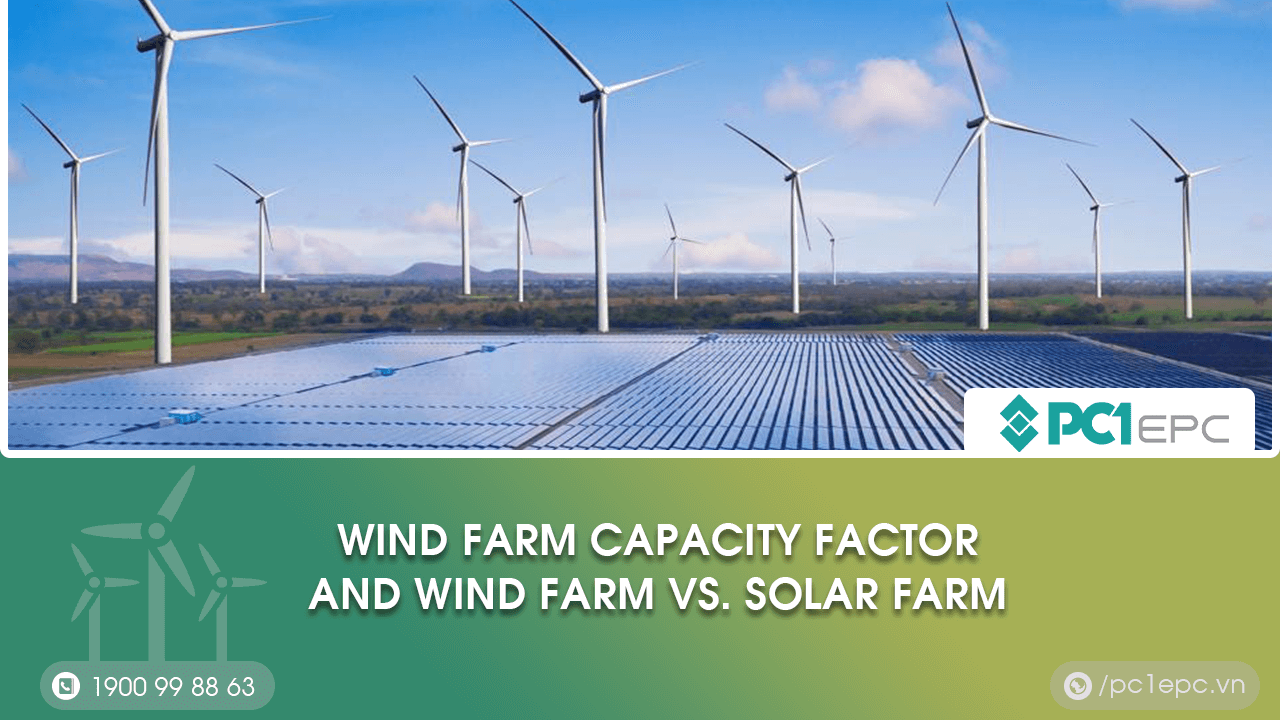
The ratio of average delivered power to theoretical maximum power is known as the capacity factor (CF) of wind power. It can be calculated for a single turbine, a wind farm with several turbines, or an entire nation with many farms.
A wind farm’s capacity factor is variable, due to the natural variability of the wind. The capacity factor for a wind farm is based on the wind speed, the swept area of the turbine, and the size of the generator. The capacity factor is also impacted by electricity demand and transmission line capacity.
What affects a wind farm capacity factor
The calculation of the capacity factor takes time and is affected by a variety of factors.
In most cases, the capacity factor is calculated over a year.
Therefore, many different causes that happen throughout the year would affect the capacity factor of the wind farm. These include wind speed, availability of wind, turbine design, air density, and others.
Wind speed
Wind speed largely determines the amount of electricity generated by the turbine. Because stronger winds allow the blades to spin faster, higher wind speeds generate more power. More mechanical and electrical energy from the generator due to faster revolutions.
Availability of wind

For renewable energy sources such as wind power, the main reason for the reduced capacity factor is generally the availability of the energy source. The wind is not always strong, consistent, or present. 24 hours a day, 365 days a year, the wind does not always blow at the same speed. A location’s wind resources can occasionally vary seasonally. Sometimes the amount of wind is determined by unforeseen weather events that occur during the day.
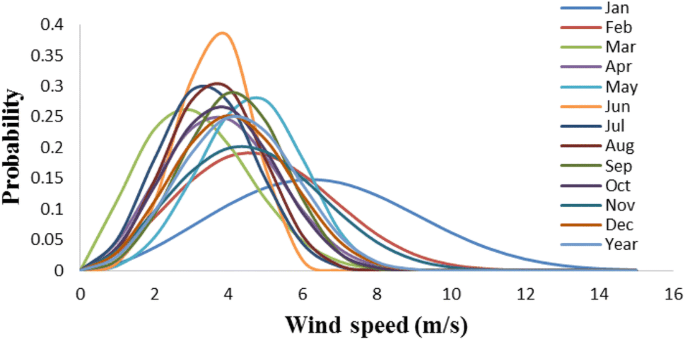
Turbine Design
Although a wind farm’s capacity factor is largely influenced by its geographic location, turbine design also plays a role.
Wind turbines are built with the rotor blade radius best achieved to maximize power output. By moving more air through the rotors, larger blades allow the turbine to capture more of the kinetic energy of the wind. Larger blades, on the other hand, require more space and higher wind speeds to function.
Air Density
According to altitude, pressure, and temperature, local air density influences power output. Dense air exerts greater pressure on the blades, resulting in increased power output.
How to improve the capacity factor of a wind turbine

The typical capacity factor of current wind farms is between 25 and 45%, but there are still ways to improve the performance.
First of all, thorough planning before constructing a wind farm can help maximize the capacity factor. It is very important to make sure that your chosen wind farm site receives optimal wind resources. This includes ensuring that there are few to no obstacles that could block incoming wind in addition to stable wind flow. The more wind resources the farm receives, the more power it can potentially generate.
Second, other factors other than wind resources also affect capacity factors. The wind turbine’s ability to capture energy from incoming wind is influenced by its design, too. Low wind speeds and turbulent wind are, in general, two major difficulties for turbine operation.
Modern wind turbines that can produce electricity at lower wind speeds, therefore, have higher capacity factors. Turbulent wind-functioning wind turbines have additional competitive advantages. To ensure the highest possible power output, it is crucial to choose the type of wind turbine that responds best to the local wind conditions.
Wind farm vs solar farm
The two most powerful sources of renewable energy are wind and solar. They produce jobs and reduce pollution. The world’s most remote areas and densest population centers receive power from them.
Since there are many factors involved, comparing solar farms to wind farms is more complicated than it first appears. Let’s check out the strong and weak points of wind and solar farms below.
Strengths & limitations of solar farms
|
Strengths |
Limitations |
| More consistently produce energy than a wind farm | Not possible to produce at night or in cloudy areas |
| Large-scale power production is possible with solar farms | Despite declining solar panel costs, up-front expenses can be high |
| After installation, panels require little upkeep. | Compared to wind turbines, solar panels produce significantly less electricity |
| In contrast to wind turbines, solar panels don’t make noise |
Strengths & limitations of wind farms
| Day or night, wind can be used for energy | Wind farms provide unpredictable energy |
| Power from wind farms can be produced in large quantities | Lightning and wind can cause damage to wind turbines |
| Wind farms can be constructed offshore | Birds and bats that fly can be harmed or killed by turbines |
| Compared to solar panels, turbines produce more electricity | Turbine may make noise |
|
Solar panels are more contaminated than turbines |
Transmission lines must be constructed to bring electricity to populated areas because wind farms are typically situated in remote areas. |
Wind farm vs. solar farm, which is the winner?

Compared to solar panels, wind turbines release less CO2 into the atmosphere, consume less energy, and produce more energy overall. But the enormous power-generating capacity of wind turbines doesn’t make wind farms a clear winner.
Wind turbines require moving parts, whereas solar panels are a stationary source of power. Solar generators require less maintenance and are significantly less expensive in the long run than their counterparts, which can be costly to maintain and repair when something goes wrong.
Of course, none of them are without their drawbacks. But in the end, combining solar and wind farms can make sense to provide consistent, clean, renewable power 24/7 if you want to live off the grid or have a lot of lands.
Summary
You must have a basic understanding of the concept of the wind farm capacity factor by reading this conclusion, which also provides the answer to the question: Which is more efficient, a wind farm or a solar farm? I hope you learned something interesting and useful from this article. Stay tuned for more updates.