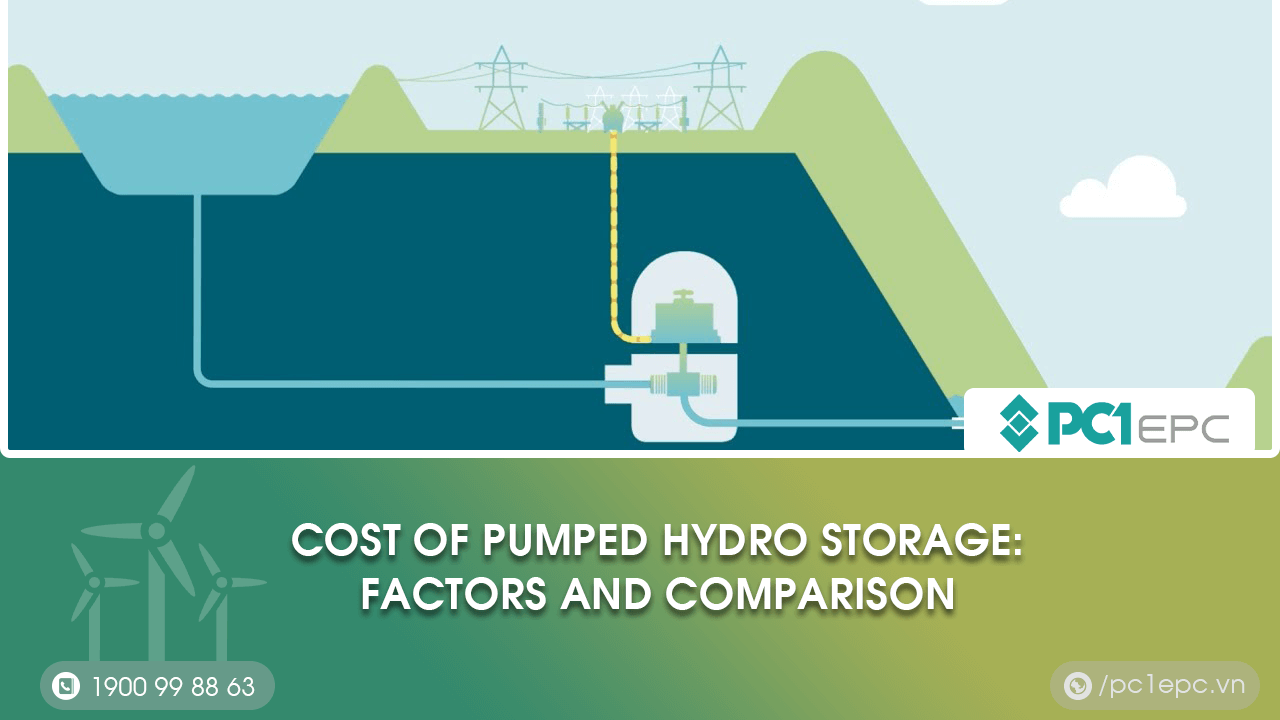
Pumped hydro storage is a technology used to store energy that is produced by renewable energy sources such as wind and solar power. It involves using electricity to pump water up to a high-level reservoir or dam. When energy is needed, the water is released back down to a lower reservoir, generating electricity through turbines. This technology acts as an energy storage “battery,” which helps to improve the reliability and efficiency of renewable energy production.
The importance of pumped hydro storage in energy production lies in its ability to address the intermittent nature of renewable energy sources. Energy from wind and solar power is not always available when needed, and pumped hydro storage provides a solution to this challenge. By storing excess energy during periods of high production, pumped hydro storage can provide a consistent supply of electricity during periods of low production. This helps to reduce the reliance on traditional energy sources such as coal and gas, while also reducing carbon emissions.
Cost of pumped hydro storage
Pumped hydro storage is a reliable and efficient technology for energy storage, but it comes at a cost. Several factors contribute to the cost of pumped hydro storage, including:
- Infrastructure: The cost of building the infrastructure, such as the dams and reservoirs, is a significant factor in the overall cost of pumped hydro storage.
- Operation and maintenance: The ongoing cost of operating and maintaining the infrastructure, including pumps, turbines, and generators, also adds to the overall cost.
- Electricity consumption: Pumped hydro storage requires electricity to pump water up to the reservoir, which can be a significant expense.
Compared to other energy storage technologies, pumped hydro storage is relatively expensive upfront but has a lower cost of operation and maintenance over its lifespan. For example, battery storage is a more expensive technology upfront but has a lower ongoing cost of operation and maintenance.
Despite the higher upfront cost, pumped hydro storage remains an attractive option for energy storage due to its reliability and long lifespan, which can range from 50 to 100 years. Additionally, pumped hydro storage can provide other benefits, such as grid stability and the ability to integrate renewable energy sources into the grid.
Benefits of pumped hydro storage
- Reliability and flexibility in energy production: Pumped hydro storage can be used as a reliable and flexible energy source, providing electricity when demand is high and storing excess energy when demand is low. This helps to balance the grid and ensure a stable and consistent energy supply.
- Reduction in carbon emissions: Pumped hydro storage is a clean energy technology that does not produce carbon emissions during operation. By storing excess energy from renewable sources such as wind and solar, it can help to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and lower carbon emissions.
- Contribution to grid stability: Pumped hydro storage can help to stabilize the grid by providing a backup source of energy during periods of high demand or when there is a sudden loss of power from other sources. This helps to prevent blackouts and brownouts and ensures a stable and reliable energy supply for homes and businesses.
Challenges and limitations of pumped hydro storage
Limited availability of suitable sites for pumped hydro storage: Pumped hydro storage requires specific geographic and geological features such as large bodies of water at different elevations, which limit the availability of suitable sites for this technology.
High upfront costs: Pumped hydro storage has high upfront costs due to the need for infrastructure such as dams, tunnels, and powerhouses. This can make it difficult to finance and implement, particularly in areas with limited financial resources.
Environmental impacts on surrounding areas: The construction of pumped hydro storage facilities can have significant environmental impacts on surrounding areas, including the displacement of wildlife, changes to water levels and quality, and disruption of ecosystems. These impacts must be carefully considered and mitigated to ensure the sustainability of the technology.
Conclusion
In summary, pumped hydro storage is a reliable and flexible energy storage technology that can contribute to grid stability and reduce carbon emissions. However, it has limited availability of suitable sites, high upfront costs, and environmental impacts that must be considered.
Despite these challenges, there is potential for future advancements and improvements in pumped hydro storage technology. Ongoing research and development could lead to more efficient and cost-effective systems, and the use of existing infrastructure such as abandoned mines could provide new opportunities for implementation.
Overall, pumped hydro storage is a promising energy storage solution with significant benefits for the transition to a clean energy future, and it should continue to be explored and developed alongside other storage technologies.
Related post: Energy storage solution provided by PC1 Group